Jar files are zipped. After unpacking you will find many .class files.
class file is an output generated by compiling Java files into bytecodes.
The Java code is not visible when you open the class file, so if you want to see it, you have to decompile it back to Java.
There are several ways to decompile, but I will introduce the following two methods here.
- How to decompile in IntelliJ IDE
- How to decompile using jd-cli tool
1. How to decompile in IntelliJ IDE
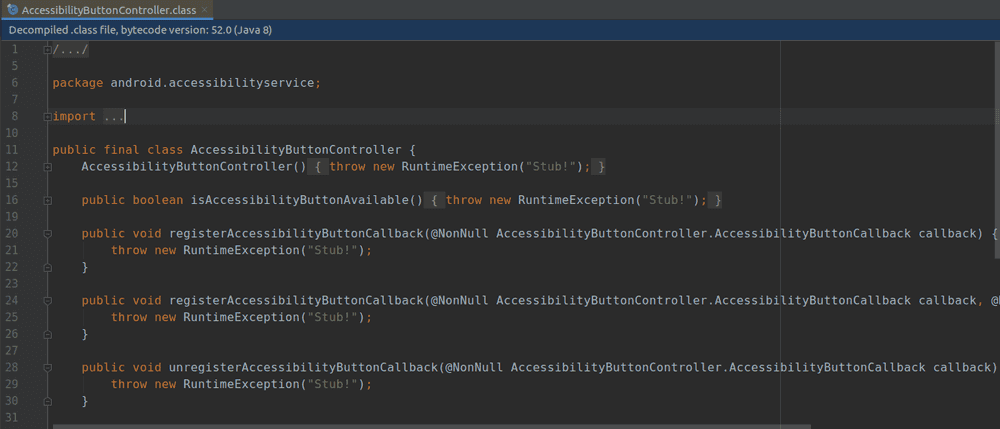
One of the easiest ways to decompile a .class file into a Java file is through IntelliJ.
If you are using IntelliJ, simply drag-and-drop the .class file onto the IDE window and it will automatically decompile to Java.
2. How to decompile using jd-cli tool
There is a tool called jd-cli that decompiles class files into Java. It is convenient because it converts all class files in the jar file to Java.
The jd-cli tool can be downloaded from GitHub - Jd-cmd.
I unzipped the installation file to ~/apps/jd-cli-0.9.2-dist/ and saved it.
Then you can run the jd-cli.jar command as follows. Just input the jar file you want to decompile and the location where the converted file is saved as an argument to the command.
$ java -jar jd-cli.jar [jar file] -od [output folder]In my case, I can decompile it with the following command: If you look in the output folder, you can see that it has been decompiled into a java file.
java -jar ~/apps/jd-cli-0.9.2-dist/jd-cli.jar android.jar -od output
$ jd-cli android.jar -od output
09:13:41.923 INFO jd.cli.Main - Decompiling android.jar
09:13:41.925 INFO jd.core.output.DirOutput - Directory output will be initialized for path output
09:13:46.225 INFO jd.core.output.DirOutput - Finished with 4751 class file(s) and 7594 resource file(s) written.Decompile only one class file
jd-cli has commands to convert class files to Java as well as jars.
- java -jar jd-cli.jar [class file] : Converts class file to java and displays it on the screen
- java -jar jd-cli.jar [class file] -od [output folder] : Converts class file to java and saves it in ouput folder
You can use it like this:
$ java -jar jd-cli.jar AbstractCollection.class
09:32:37.885 INFO jd.cli.Main - Decompiling /home/js/Desktop/android/java/util/AbstractCollection.class
package java.util;
import androidx.annotation.RecentlyNonNull;
import androidx.annotation.RecentlyNullable;
public abstract class AbstractCollection<E>
....alias (For linux user)
Since it is cumbersome to enter a command every time, you can register the command as an alias in ~/.bashrc as shown below.
$ alias jd-cli='java -jar ~/apps/jd-cli-0.9.2-dist/jd-cli.jar'If you register an alias, you can decompile it with a short command as follows.
$ jd-cli android.jar -od outputRelated Posts
- Java - Remove items from List while iterating
- Java - How to find key by value in HashMap
- Java - Update the value of a key in HashMap
- Java - How to put quotes in a string
- Java - How to put a comma (,) after every 3 digits
- BiConsumer example in Java 8
- Java 8 - Consumer example
- Java 8 - BinaryOperator example
- Java 8 - BiPredicate Example
- Java 8 - Predicate example
- Java 8 - Convert Stream to List
- Java 8 - BiFunction example
- Java 8 - Function example
- Java - Convert List to Map
- Exception testing in JUnit
- Hamcrest Collections Matcher
- Hamcrest equalTo () Matcher
- AAA pattern of unit test (Arrange/Act/Assert)
- Hamcrest Custom Matcher
- Hamcrest Text Matcher
- Why Junit uses Hamcrest
- Java - ForkJoinPool
- Java - How to use Futures
- Java - Simple HashTable implementation
- Java - Create a file in a specific path
- Java - Mockito의 @Mock, @Spy, @Captor, @InjectMocks
- Java - How to write test code using Mockito
- Java - Synchronized block
- Java - How to decompile a ".class" file into a Java file (jd-cli decompiler)
- Java - How to generate a random number
- Java - Calculate powers, Math.pow()
- Java - Calculate the square root, Math.sqrt()
- Java - How to compare String (==, equals, compare)
- Java - Calculate String Length
- Java - case conversion & comparison insensitive (toUpperCase, toLowerCase, equalsIgnoreCase)