Jetpack 또는 AAC(Android Architecture Component) Lifecycle은 액티비티의 상태에 따라 처리되는 코드를 쉽게 관리할 수 있게 도와주는 라이브러리입니다. Lifecycle을 사용하면 기존 코드를 더 읽기 쉽고, 관리하기 쉬운 코드로 만들 수 있습니다.
보통 어떤 서비스에 리스너를 등록하여 정보를 받을 때, 액티비티가 실행 중일 때 register하고 멈추었을 때 unregister를 하도록 구현을 합니다.
다들 Activity.onResume에 register를, Activity.onPause unregister코드를 작성한 경험이 있으실텐데요.
Lifecylce은 이 코드들을 옵저버 객체로 옴길 수 있도록 도와줍니다. 그래서 액티비티 코드를 복잡하지 않고 간결하게 유지하는데 도와줍니다.
Lifecycle의 주요 클래스는 다음과 같습니다.
- Livecycle: Lifecylce을 나타내는 객체입니다.
- LivecycleOwner: Activity객체를 말하며 Lifecycle객체에 액티비티 상태를 제공해줍니다.
- LifecycleObserver: Lifecylce로부터 액티비티 상태변화에 대한 이벤트를 받습니다.
LifecycleOwner, Lifecycle
LifecycleOwner는 Activity를 의미하고, 내부에 Lifecycle을 갖고 있습니다.
Lifecycle은 액티비티의 상태를 저장하고 옵저버들에게 상태변화를 알려줍니다.
Lifecycle 상태를 알고 싶다면 LifecycleObserver를 생성하고 Lifecycle에 등록을 하면 됩니다.
이해를 돕기 위해 옵저버 객체를 생성하여 Lifecycle에 등록해보는 예제코드를 작성해보겠습니다.
프로젝트 생성
Kotlin과 Use AndroidX artifacts를 선택해주세요.
(Android Studio 버전이 3.4 미만이라면 Use AndroidX artifacts옵션이 없습니다. 마이그레이션을 하거나 코드를 변경해줘야 합니다)
AndroidX로 프로젝트를 생성하지 않았다면, 메뉴에서 [Refactor] -> [Migrate to AndroidX...] 를 누르시면 AndroidX를 사용하는 프로젝트로 마이그레이션이 됩니다.
AndroidX를 사용하지 않고 Android Support Library를 사용하는 경우 사용하는 클래스의 package name이 다를 수 있습니다.
LifecycleObserver 객체 구현
Lifecycle의 상태를 받고 싶으면 Observer를 먼저 구현해야 합니다.
아래와 같이 MyObserver.kt파일을 생성하고 LifecycleObserver를 상속한 MyObserver를 구현하였습니다.
class MyObserver(private val lifeCycle: Lifecycle) : LifecycleObserver {
companion object {
const val TAG = "MyObserver"
}
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_CREATE)
fun onCreated(source: LifecycleOwner) {
Log.d(TAG, "onCreated")
}
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_START)
fun onStart() {
Log.d(TAG, "onStart")
if (lifeCycle.currentState.isAtLeast(Lifecycle.State.INITIALIZED)) {
Log.d(TAG, "currentState is greater or equal to INITIALIZED")
}
if (lifeCycle.currentState.isAtLeast(Lifecycle.State.CREATED)) {
Log.d(TAG, "currentState is greater or equal to CREATED")
}
if (lifeCycle.currentState.isAtLeast(Lifecycle.State.STARTED)) {
Log.d(TAG, "currentState is greater or equal to STARTED")
}
if (lifeCycle.currentState.isAtLeast(Lifecycle.State.RESUMED)) {
Log.d(TAG, "currentState is greater or equal to RESUMED")
}
if (lifeCycle.currentState.isAtLeast(Lifecycle.State.DESTROYED)) {
Log.d(TAG, "currentState is greater or equal to DESTROYED")
}
}
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_RESUME)
fun onResume() {
Log.d(TAG, "onResume")
}
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_PAUSE)
fun onPause() {
Log.d(TAG, "onPause")
}
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_STOP)
fun onStop() {
Log.d(TAG, "onStop")
}
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_DESTROY)
fun onDestroy() {
Log.d(TAG, "onDestroy")
}
}코드를 보시면 onCreated처럼 각 상태에 따른 메소드들을 만들어 주었습니다.
그리고 @OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_CREATE)처럼 Annotation을 붙여주었습니다.
여기서 Annotation을 붙이는 것은 중요합니다. Lifecycle객체는 상태변화를 알려줄 때 annotation이 붙은 함수를 호출해줍니다. 이 코드가 컴파일될 때 annotation을 보고 호출해주는 코드가 자동 생성됩니다.
예를들어 Lifecycle.Event.ON_CREATE는 Lifecycle 상태가 CREATE일 때 호출됩니다.
다른 상태들도 이름을 보면 언제 호출되는지 짐작할 수 있습니다.
옵저버 등록
위에서 설명드린 것처럼 AppCompatActivity는 내부적으로 LifecycleOwner를 구현하고 있습니다. 그렇기 때문에 Activity는 lifecycle 객체를 직접 참조할 수 있습니다.
아래 코드처럼 옵저버를 생성할 때 인자로 lifecycle을 넘겨줍니다.
lifecycle을 전달해주면 옵저버에서 lifecycle에 접근하여 현재 상태를 알 수 있습니다.
옵저버 객체를 생성했다면, lifecycle.addObserver로 옵저버 추가가 가능합니다.
class LifeCycleActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private var observer = MyObserver(lifecycle)
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_lifecycle)
lifecycle.addObserver(observer)
}
}옵저버 등록을 마쳤습니다. 내부적으로 액티비티의 상태가 변경되면 Lifecycle로 전달되고 Lifecycle은 옵저버들에게 상태를 알려줍니다.
결과 확인
앱을 직접 실행해보시고, 액티비티의 상태가 어떨 때 옵저버의 어떤 메소드가 호출되는지 확인해보세요.
액티비티가 실행(resume)되면 출력되는 로그입니다.
MyObserver: onCreated
MyObserver: onStart
MyObserver: currentState is greater or equal to INITIALIZED
MyObserver: currentState is greater or equal to CREATED
MyObserver: currentState is greater or equal to STARTED
MyObserver: currentState is greater or equal to DESTROYED
MyObserver: onResume액티비티가 종료되면(stop)되면 출력되는 로그입니다.
MyObserver: onPause
MyObserver: onStop보신 것처럼 액티비티의 상태가 변경되면 annotation이 설정된 메소드가 호출됩니다. annotation으로 설정하는 이벤트 종류는 다음과 같은 것들이 있습니다.
public enum Event {
ON_CREATE,
ON_START,
ON_RESUME,
ON_PAUSE,
ON_STOP,
ON_DESTROY,
ON_ANY
}동적으로 Lifecycle의 상태를 알아야 할 때도 있습니다.
lifeCycle.currentState로 현재상태를 알 수 있습니다.
옵저버에서 사용한 코드 State.isAtLeast는 상태를 점수로 표현하고 현재의 위치가 어떤 상태보다 큰지 boolean으로 리턴해주는 함수입니다.
STARTED는 DESTROYED, INITIALIZED, CREATED 보다 큰 값을 갖고 있습니다.
만약 STARTED 이상의 상태에서만 초기화가 필요하다면 State.isAtLeast를 사용하여 구현할 수 있습니다.
/**
* Lifecycle states. You can consider the states as the nodes in a graph and
* {@link Event}s as the edges between these nodes.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")
public enum State {
/**
* Destroyed state for a LifecycleOwner. After this event, this Lifecycle will not dispatch
* any more events. For instance, for an {@link android.app.Activity}, this state is reached
* <b>right before</b> Activity's {@link android.app.Activity#onDestroy() onDestroy} call.
*/
DESTROYED,
/**
* Initialized state for a LifecycleOwner. For an {@link android.app.Activity}, this is
* the state when it is constructed but has not received
* {@link android.app.Activity#onCreate(android.os.Bundle) onCreate} yet.
*/
INITIALIZED,
/**
* Created state for a LifecycleOwner. For an {@link android.app.Activity}, this state
* is reached in two cases:
* <ul>
* <li>after {@link android.app.Activity#onCreate(android.os.Bundle) onCreate} call;
* <li><b>right before</b> {@link android.app.Activity#onStop() onStop} call.
* </ul>
*/
CREATED,
/**
* Started state for a LifecycleOwner. For an {@link android.app.Activity}, this state
* is reached in two cases:
* <ul>
* <li>after {@link android.app.Activity#onStart() onStart} call;
* <li><b>right before</b> {@link android.app.Activity#onPause() onPause} call.
* </ul>
*/
STARTED,
/**
* Resumed state for a LifecycleOwner. For an {@link android.app.Activity}, this state
* is reached after {@link android.app.Activity#onResume() onResume} is called.
*/
RESUMED;
/**
* Compares if this State is greater or equal to the given {@code state}.
*
* @param state State to compare with
* @return true if this State is greater or equal to the given {@code state}
*/
public boolean isAtLeast(@NonNull State state) {
return compareTo(state) >= 0;
}
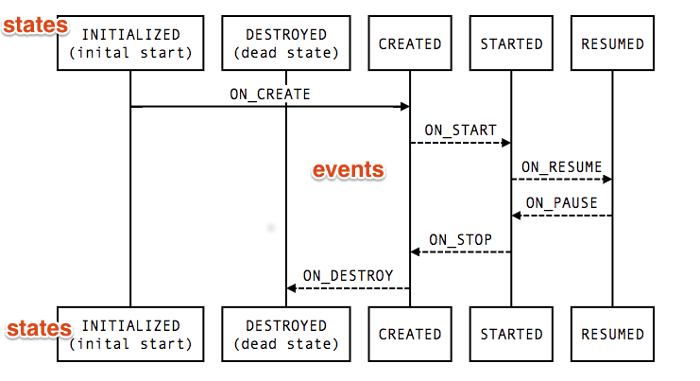
}위의 이벤트(Event)와 상태(State)의 관계를 그래프로 표현한 그림입니다. 각각의 상태에 따라 어떤 이벤트가 전달되는지 알려줍니다.
정리
Lifecycle과 LifecycleOwner에 대해서 간략히 알아보았고, 옵저버를 생성하여 상태를 받는 코드를 작성해보았습니다.
Jetpack Lifecycle 구현 및 구조에 대한 자세한 내용은 Android Jetpack Lifecycle 구조 분석을 참고해주세요.
참고
- 샘플 코드는 GitHub에 있습니다(step1 참고)
- Jetpack Lifecycle - Android
Related Posts
- Android 14 - 사진/동영상 파일, 일부 접근 권한 소개
- Android - adb push, pull로 파일 복사, 다운로드
- Android 14 - 암시적 인텐트 변경사항 및 문제 해결
- Jetpack Compose - Row와 Column
- Android 13, AOSP 오픈소스 다운로드 및 빌드
- Android 13 - 세분화된 미디어 파일 권한
- Android 13에서 Notification 권한 요청, 알림 띄우기
- Android 13에서 'Access blocked: ComponentInfo' 에러 해결
- 에러 해결: android gradle plugin requires java 11 to run. you are currently using java 1.8.
- 안드로이드 - 코루틴과 Retrofit으로 비동기 통신 예제
- 안드로이드 - 코루틴으로 URL 이미지 불러오기
- Android - 진동, Vibrator, VibrationEffect 예제
- Some problems were found with the configuration of task 에러 수정
- Query method parameters should either be a type that can be converted into a database column or a List
- 우분투에서 Android 12 오픈소스 다운로드 및 빌드
- Android - ViewModel을 생성하는 방법
- Android - Transformations.map(), switchMap() 차이점
- Android - Transformations.distinctUntilChanged() 소개
- Android - TabLayout 구현 방법 (+ ViewPager2)
- Android - 휴대폰 전화번호 가져오는 방법
- Android 12 - Splash Screens 알아보기
- Android 12 - Incremental Install (Play as you Download) 소개
- Android - adb 명령어로 bugreport 로그 파일 추출
- Android - adb 명령어로 App 데이터 삭제
- Android - adb 명령어로 앱 비활성화, 활성화
- Android - adb 명령어로 특정 패키지의 PID 찾기
- Android - adb 명령어로 퍼미션 Grant 또는 Revoke
- Android - adb 명령어로 apk 설치, 삭제
- Android - adb 명령어로 특정 패키지의 프로세스 종료
- Android - adb 명령어로 screen capture 저장
- Android - adb 명령어로 System 앱 삭제, 설치
- Android - adb 명령어로 settings value 확인, 변경
- Android 12 - IntentFilter의 exported 명시적 선언
- Android - adb 명령어로 공장초기화(Factory reset)
- Android - adb logcat 명령어로 로그 출력